Table of Contents
Name of Procedure
- Shoulder subacromial bursa injection (with or without steroid) with fluoroscopy
Sample Opnote
The Quick Guide
Goal
To inject a medication into the subacromial bursa
Indications
Depending on what’s injected, usually it is to treat pain from bursitis
Contraindications
Anatomy
For the purposes of a bursa injection, anatomy is straightforward. From an anterior perspective the bursa is just near the tip of the shoulder. Since this is fluoroscopically guided you’ll use the acromion as your landmark under fluoro to get an exact location.

Equipment/Skills
- C-Arm
- Bed for C-Arm
- 25g x 1.5″ hypodermic needle
- Contrast
- 1 or 2 3cc syringes (may not need as noted below)
- Desired injectate:
- bupivacaine/lidocaine
- supartz/synvisc/orthovisc
- steroid (dexamethasone/triamcinalone)
- prep solution
- drape to keep injection site clean
Landmarks and Patient Positioning
- Position the patient in a basic supine position so that the bottom of the c-arm can go under the table below the shoulder.
- Extend the arm on the ipsilateral side to open up the joints as much as possible.
Technique
- Position the C-arm in an AP orientation.
- Playing with the angle will allow you to see which angle is best. But you generally want the acromion well delineated and no lying “over” the other bony structures, as seen in the image below.
- Use a pointer to find a spot directly under the acromion.
- Insert a 25g x 3.5 inch needle in a mostly AP direction. By starting a little bit below the acromion you can aim a bit superior till you contact the acromion as a landmark.
- Then walk inferior till it passes under and you should be in the bursa.
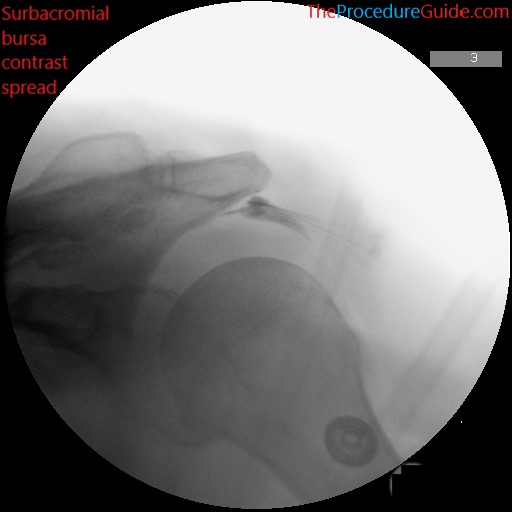
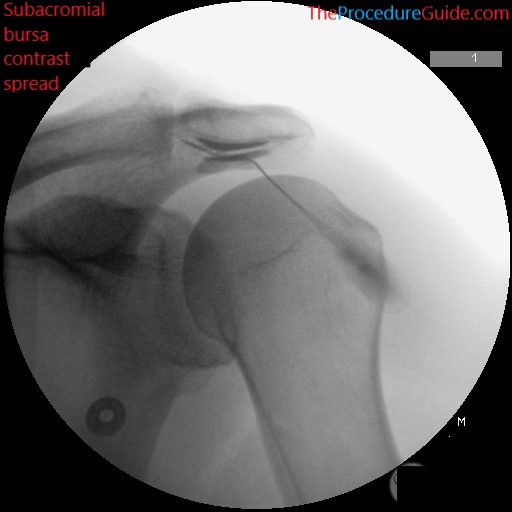
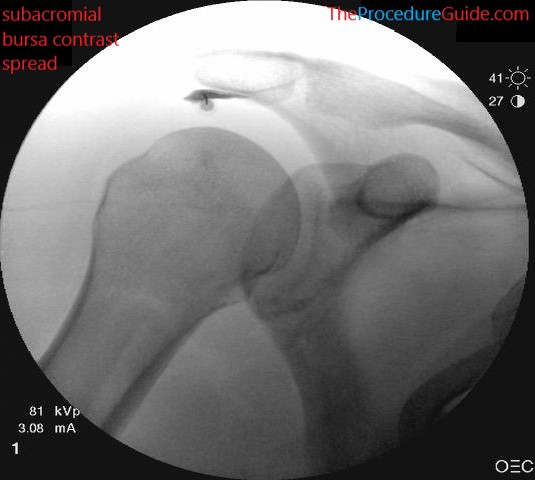
- Inject a small amount of contrast to confirm bursa spread as noted.
- From here inject the desired medication based on the specific procedure that you’re doing
Tips
- Usually a 25g x 1.5″ hypodermic needle is sufficient to enter any space in the shoulder. With this approach no second/larger needle is needed, and usually it can be done without local anesthetic since it’s the same needle that would be used to administer local anesthetic anyway.
- If it turns out that the hypodermic needle is not long enough, just inject lidocaine through it while pulling out.
- Then use a longer needle such as a bent quincke needle to reach the joint space.
