Table of Contents
Name of Procedure
Fluoroscopic guided piriformis muscle injection
Sample Opnote
Goal
Inject medication into the piriformis muscle for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
Indications
Piriformis syndrome
Contraindications
- Common contraindications
- Blood thinners – See ASRA based guidelines (and an abbreviated protocol) for managing various blood thinners pre and post procedure
Anatomy
The piriformis runs from the sacrum to greater trochanter of the femur.
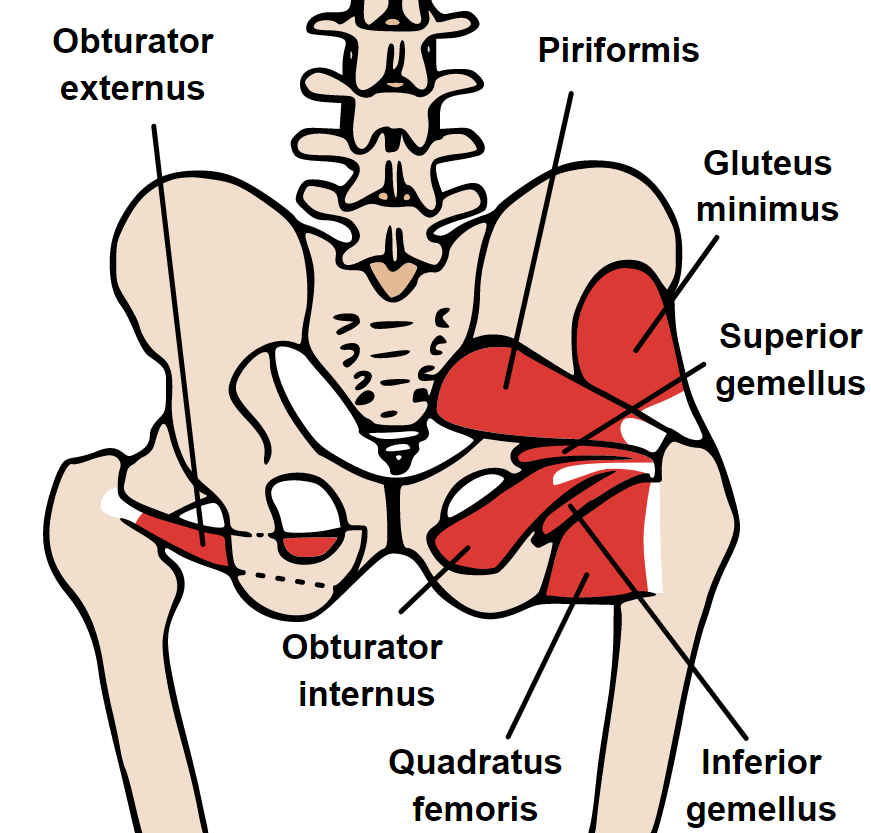
The sciatic nerve can have a variable relationship with the muscle but spasm, trigger point, pathology, etc around the piriformis muscle can affect the nerve causing sciatica pain.

Equipment/Skills/Setup
Core Equipment/Disposables: See our disposables/equipment article for “core” items that are common to all procedures.
Special items and suggested setup for this procedure:
- 22g x 5” quincke needle (a 3.5” needle can also be used in most patients but might not be long enough in some patients)
- 2-3cc local anesthetic (such as dilute 0.125% bupivacaine) and desired steroid (such as dexamethasone 10mg) in 5cc syringe as primary injectate
- 3cc contrast
- 3-5cc 1% lidocaine in 5cc syringe with 25g x 1.5″ hypodermic needle for subcutaneous anesthetic
Landmarks and Patient Positioning
Position the patient in a basic prone position so that the bottom of the c-arm can go under the table below the hip/sacrum on the treatment side.
Technique
The primary goal is to place the needle tip anywhere in the piriformis muscle, but we’ll focus on trying to catch it just above the head of the femur.
- Identify a spot just above your target, marked with the red dot.
- Anesthetize in the skin and in a fan like fashion going deeper in case you need to direct your needle to a different location.
- Insert the needle straight anteriorly till it hits bone.
- Pull the needle back slightly and then inject contrast.
- Once appropriate spread is confirmed, inject your desired medication.
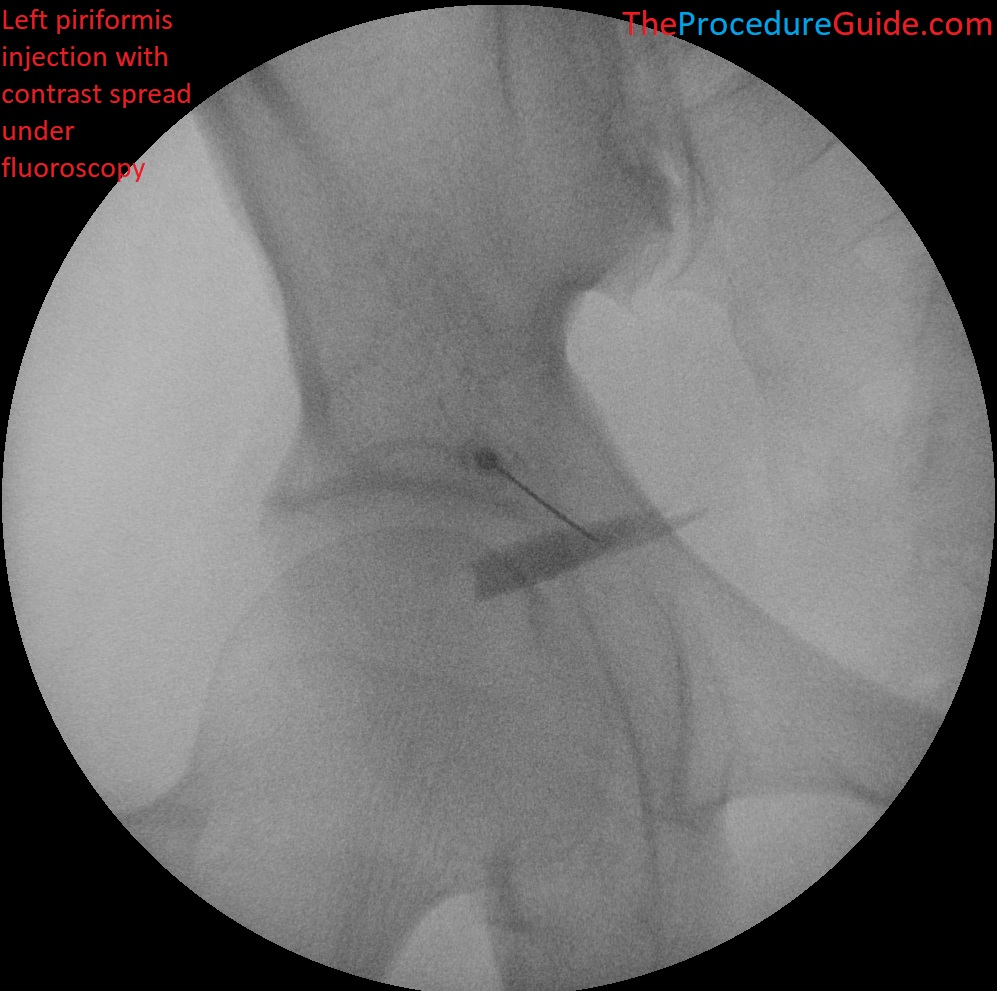
Fluoroscopic guided piriformis injection with contrast spread
Tips
The procedure is generally very straightforward and the most common issue will be getting the needle into the muscle and getting adequate spread.
- Via fluoroscopy you don’t really know if you are entering the muscle. To some extent it’s needle redirection (trial) and contrast injection (error) to test if you’re in the right spot.
- Knowing the course of the muscle can help you with this.
References
- Piriformis Injection: An Ultrasound-Guided Technique
- Review of piriformis syndrome and an ultrasound guided technique with real world and ultrasound images.
- UG PIRIFORMIS INJECTION
- Ultrasound technique (no verbal commentary but good side by side anatomy)
- Piriformis Injection
- Mostly a review of piriformis syndrome and some basic description of the procedure.

